Copy-Edit 3 Protocol in 101sec
Learn 3 protocol in 101 sec
Copy-Edit 3 Protocol in 101sec
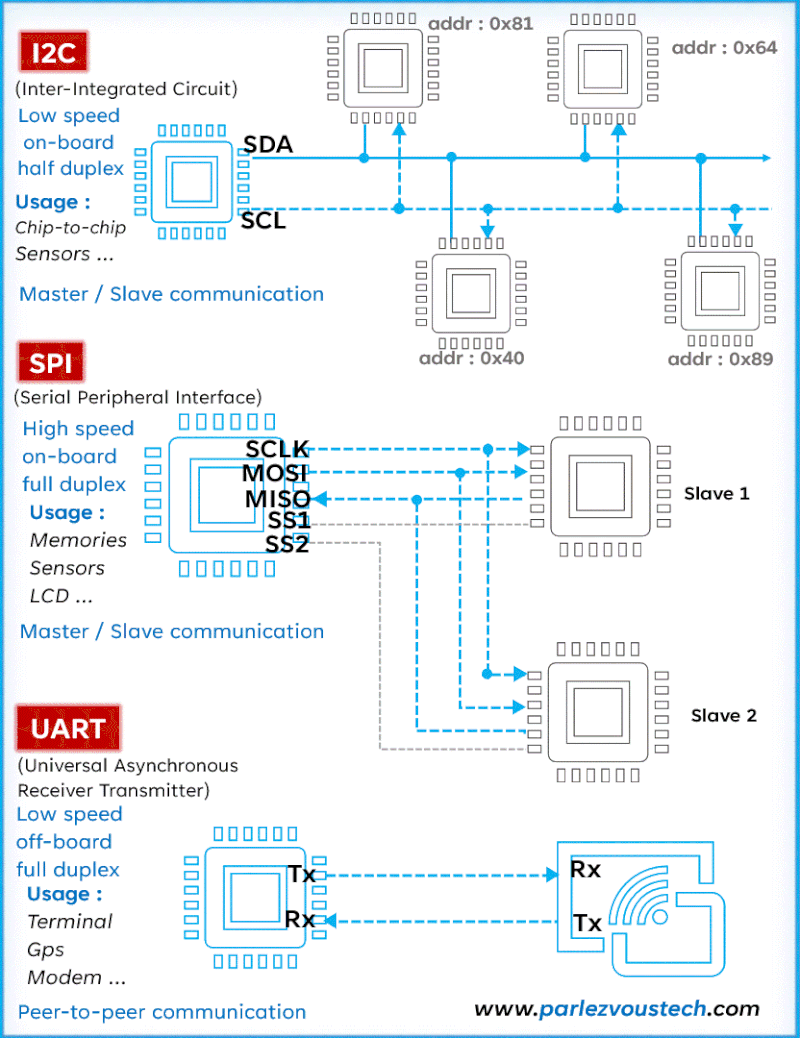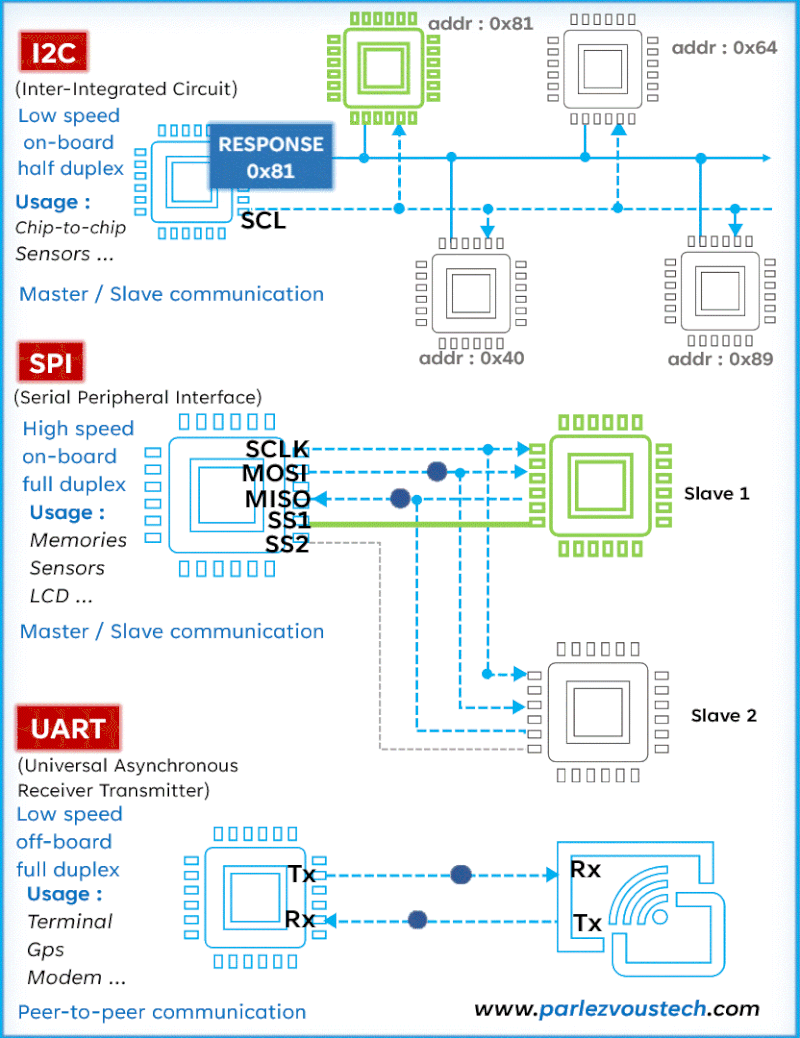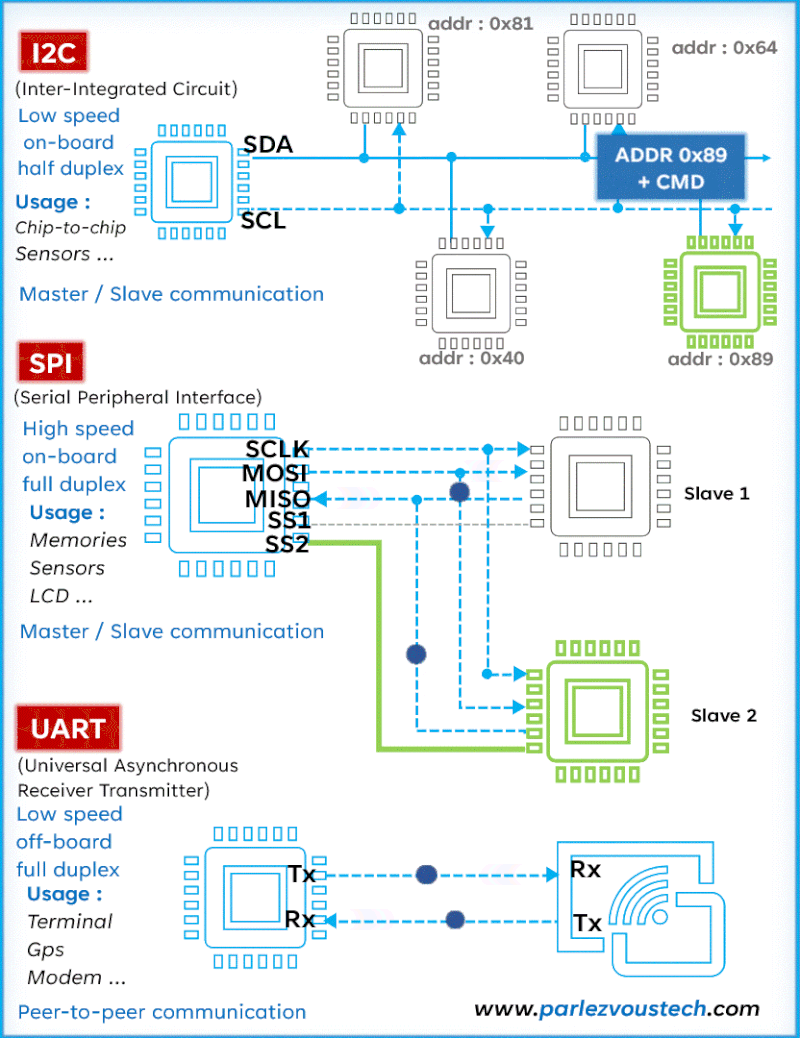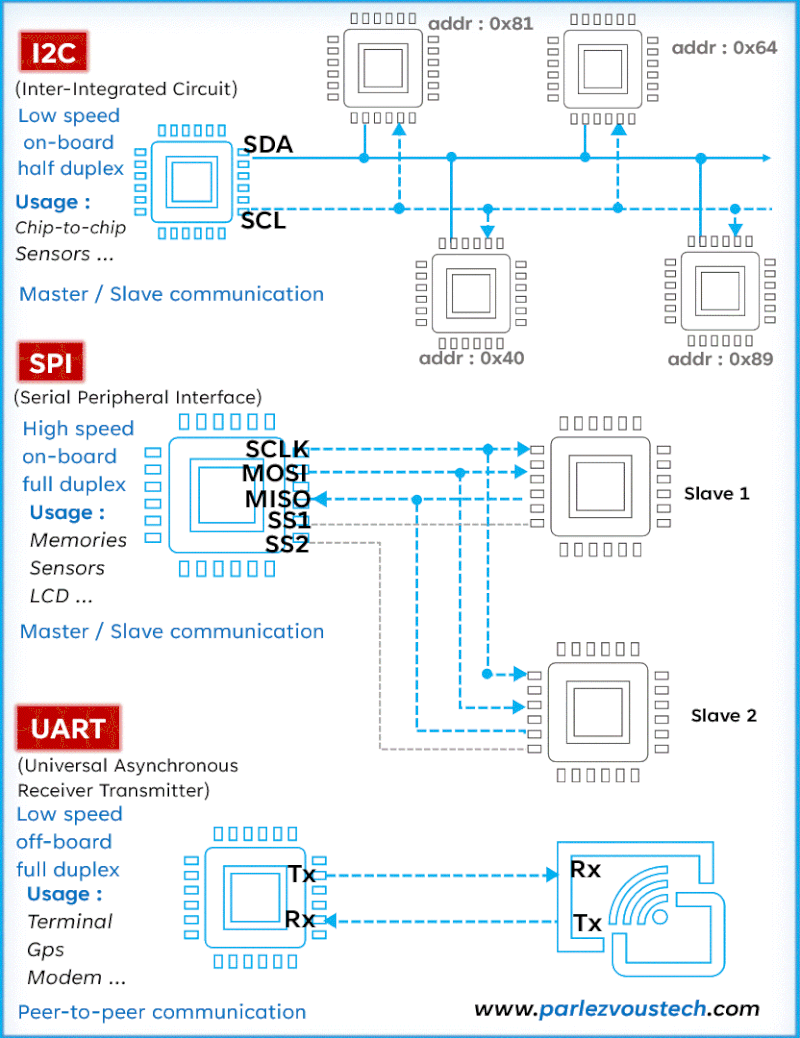
Comparison of SPI, I2C, and UART Protocols
| Feature | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) | I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) | UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Full Duplex (data can be transmitted and received simultaneously) | Half Duplex (data is transmitted in one direction at a time) | Asynchronous (no clock signal, data transmitted one byte at a time) |
| Speed | Very fast, up to several Mbps (e.g., 10+ Mbps) | Moderate, typically up to 400 Kbps (but can go up to 3.4 Mbps in fast mode) | Relatively slow, typically up to 1 Mbps |
| Number of Wires | 4 wires: MOSI, MISO, SCLK, SS (Chip Select) | 2 wires: SDA (Data) and SCL (Clock) | 2 wires: TX (Transmit) and RX (Receive) |
| Data Addressing | No addressing; uses Chip Select (CS) to choose slave devices | Addressing used; devices are identified by unique addresses | No addressing; direct communication between two devices |
| Master-Slave | Supports multi-master and multi-slave configurations | Supports multi-master and multi-slave configurations, but more common with one master and multiple slaves | One-to-one communication (one transmitter, one receiver) |
| Error Checking | No built-in error checking; may rely on software | Includes ACK/NACK for error checking | Parity bit can be used for error checking |
| Example Usage | - High-speed communication between microcontrollers and sensors - SD cards, TFT displays - Example: Connecting a temperature sensor to a microcontroller | - Low-speed communication between a master (e.g., microcontroller) and multiple peripherals - EEPROM, RTC modules - Example: Connecting a real-time clock (RTC) module to a microcontroller | - Serial communication between a computer and a microcontroller - GPS modules, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi modules - Example: UART-based communication between a GPS module and a microcontroller |
Key Points in the Table
- SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface): Full-duplex, fast communication for short distances, no addressing.
- I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit): Half-duplex, moderate speed, supports addressing for multiple devices.
- UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter): Asynchronous, often slower, used for communication between devices like computers and microcontrollers.
🙏 Thanks to PARLEZVOUSTECH
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.